The joint project “ChaRiUT“ - Characterization of branched cracks in dissimilar welded joints using modern ultrasonic methods with regard to the reliability assessment of components - is intended to provide the basis for adapted assessment concepts for the safety of nuclear facilities.
Many components in nuclear facilities are exposed to corrosive conditions and mechanical loads. Stress corrosion cracking can cause damage that impairs the integrity of highly stressed systems. This research project focuses on dissimilar welded joints of austenitic and ferritic steels, such as those used in pipelines in the primary circuit of nuclear facilities.
Ultrasonic methods have proven themselves for many years in the quality testing of welded joints, and their use is regulated in numerous standards and test instructions. Research projects continuously ensure that the latest technology is used and that the high reliability requirements for the process, which are necessary in nuclear technology, are met at the same time. Austenitic dissimilar welds are particularly difficult to test using acoustic methods, as the weld metal area is very wide and exhibits both elastic anisotropy and inhomogeneity, thus strongly influencing sound propagation.
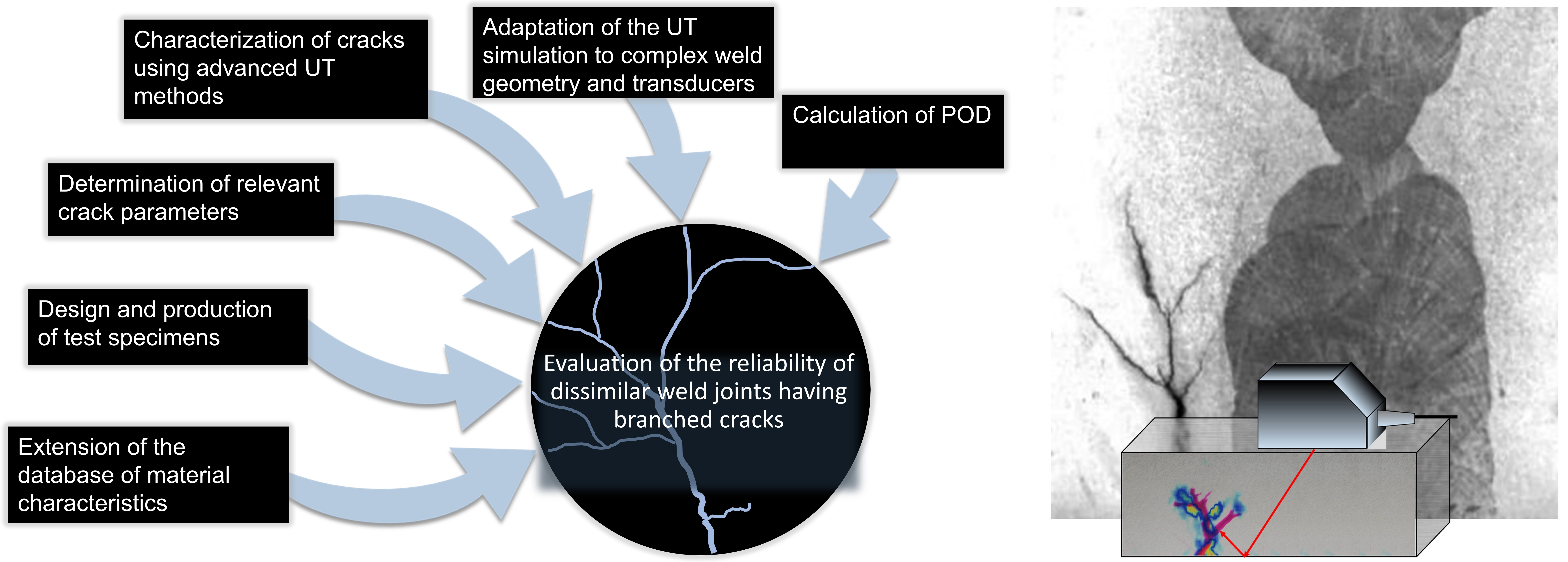
The overall aim of the ChaRiUT project is to further develop ultrasonic methods in order to characterize various relevant crack features of multi-branched stress corrosion cracks in dissimilar welded joints quantitatively and as accurately as possible. The cooperation partners Materialprüfungsanstalt University Stuttgart (MPA) and Fraunhofer Institute for Nondestructive Testing IZFP are pursuing different, coordinated sub-goals.
The MPA is concerned with the production of a test body set with branched cracks and the determination of relevant properties of branched cracks for the probability of failure. Both research institutes use different ultrasonic methods, with Fraunhofer IZFP concentrating on the characterization of weld seam properties and material discontinuities using the extended ultrasonic total focusing method (TFM) in the sub-project “Development of Extended Ultrasonic Methods“. Adapted reconstruction methods are to be developed for the characterization of branched cracks in dissimilar welded joints. Simulation calculations will also be used for this purpose. The project will also calculate probability of detection (POD) curves as an input variable for reliability assessment.
 Fraunhofer Institute for Nondestructive Testing IZFP
Fraunhofer Institute for Nondestructive Testing IZFP