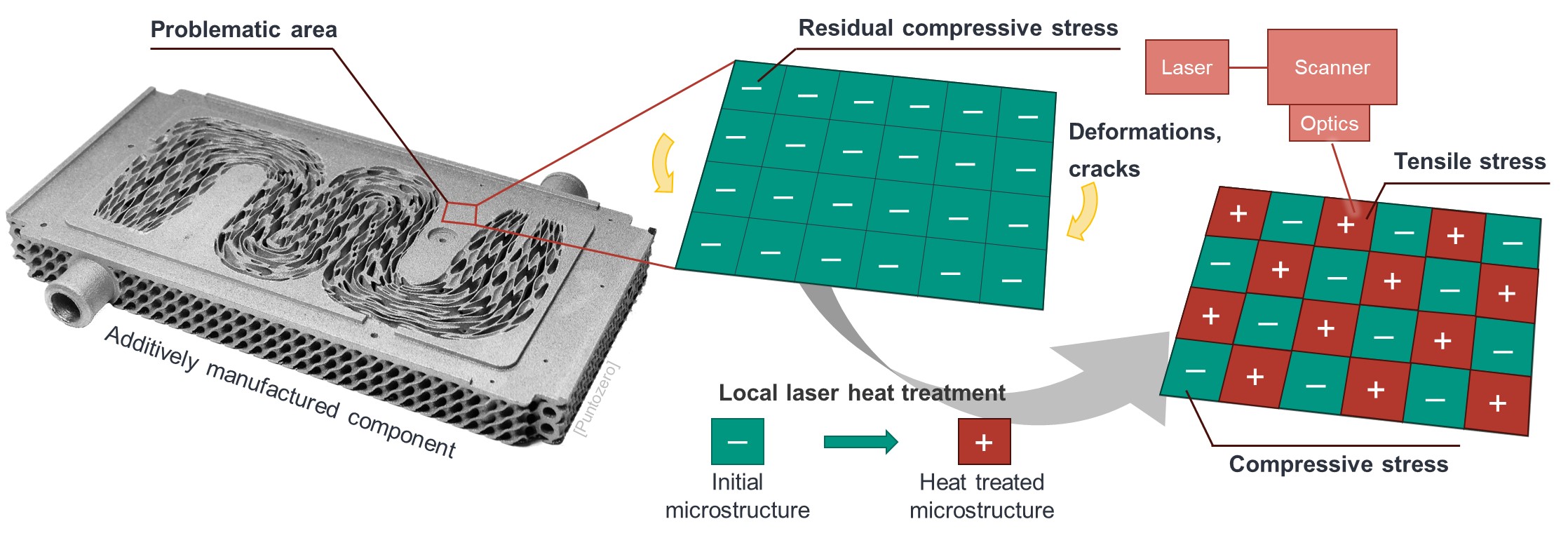
The efficiency of electrolysers, especially in the context of the energy transition and the hydrogen economy, is largely dependent on temperature control in the electrolysis process. Heat exchangers play a decisive role here. Conventionally, such heat exchangers are usually manufactured manually, especially for new developments and small series, which is extremely time-consuming and can result in quality fluctuations. Additive manufacturing processes such as laser powder bed fusion (PBF-LB/M) represent a promising alternative to manual production. They enable complex surface structures for optimum heat transfer with consistent production quality. However, one challenge with PBF-LB/M is the formation of unfavorable residual stress distributions, which can lead to cracks and distortion in later component use, particularly in the high-performance steels used in heat exchangers.
The aim of the research project is therefore to generate favorable residual stress distributions in the component by using the process laser for targeted heat treatment of individual component areas during the layer build-up of the additive manufacturing process. In this way, distortion and crack-free, dimensionally stable heat exchangers can be produced with PBF-LB/M. In order to monitor the result of the local heat treatment and the associated residual stress changes with spatial and temporal resolution during the layer build-up and thus control the laser heat treatment process, a novel sensory in-process measurement method is being developed. This new measuring method poses a particular challenge. On the one hand, it must be sensitive to local structural changes in the component, be able to be integrated into the installation space of the PBF-LB/M system and be robust enough to allow measurements during layer build-up.
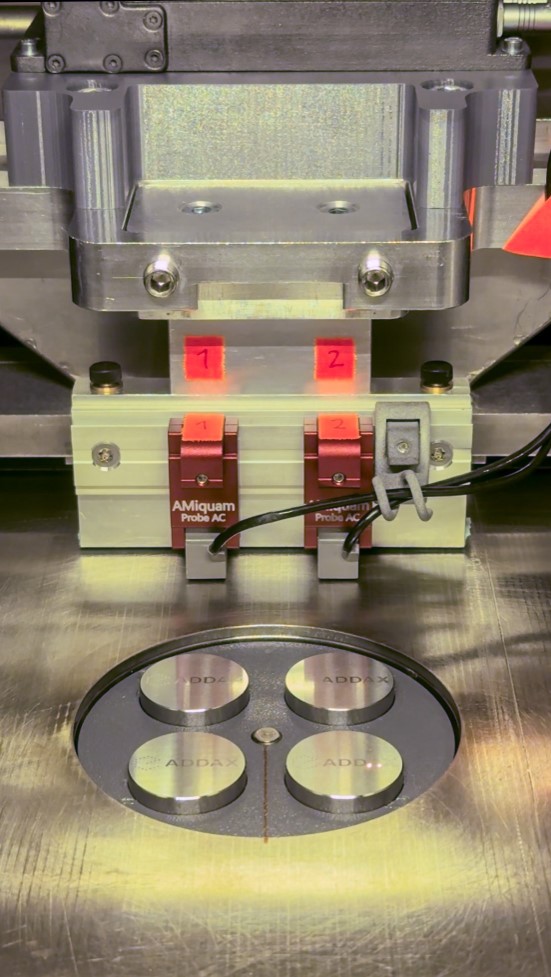
The basis for this are integrable eddy current sensors, which are being further developed to meet the special requirements of this application.
Approach:
- Development and implementation of a process-integrated, eddy current-based measurement technology
- Development of empirical models to describe the relationships between laser processing, structural changes and residual stresses
- Production of components with targeted, local heat treatment of the material
- Validation of component properties using destructive reference methods
 Fraunhofer Institute for Nondestructive Testing IZFP
Fraunhofer Institute for Nondestructive Testing IZFP